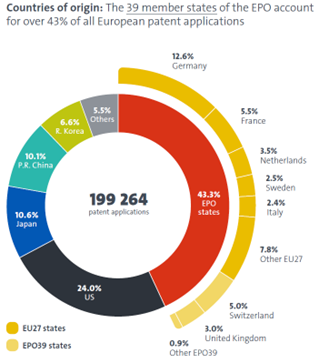
27.3% of all applications filed at the European Patent Office (EPO) in 2024 originated from China, Japan, and Korea. Almost all of such applications claim priority from patent applications filed locally in those countries, which are normally prepared and filed in the local languages. This means that the content of such applications must be translated into an EPO official language (normally English) either when a corresponding European patent application is filed or a PCT application enters the regional phase.
The intricacies of translation
Translation issues can invalidate patents in Europe. Priority claims are only valid if a priority document contains a clear and unambiguous disclosure of a claimed invention. This is a very strict test and minor differences in language can lead to allegations that a claimed invention was not disclosed in an earlier priority application.
Similarly, when a European patent application is derived from a PCT application, whether or not matter is added during prosecution is judged against the content of the original PCT application rather than the content of a translation filed on entry to the regional phase. Again, the EPO’s test for added matter is a strict one – did the original PCT application contain a clear and unambiguous disclosure of a claimed invention? Minor changes in language can result in a patent application failing such a test.
Whenever such issues arise, the EPO is forced to consider the content of documents written in languages other than the working languages of the office. When dealing with languages such as Chinese, Japanese and Korean which are far removed from the European languages with which the EPO is normally familiar, knowledge of how languages work and the quality of translations used can become crucial.
The Opposition against EP2022349
The Opposition against EP2022349, filed by seven Opponents, illustrates how unsatisfactory translations can jeopardise the validity of patents before the EPO.
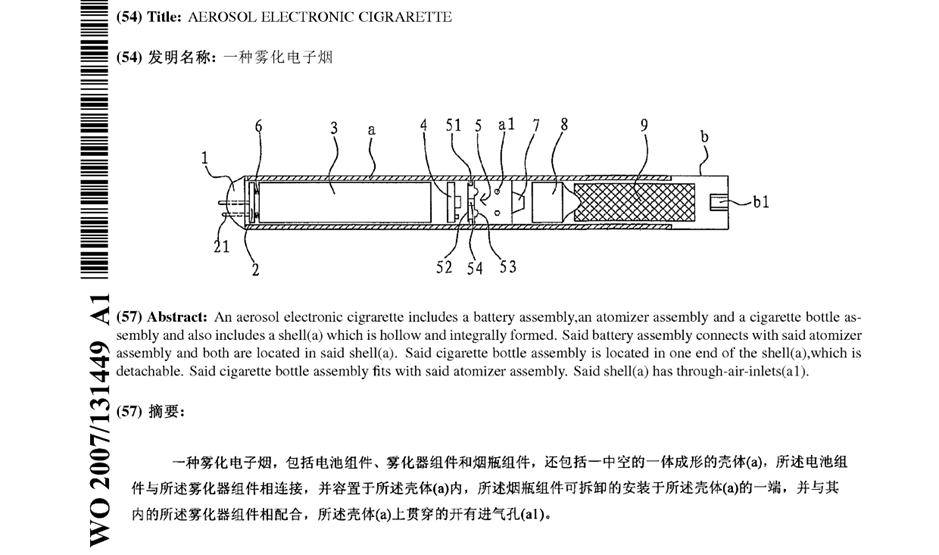
EP2022349 relates to an early vaporiser design for electronic cigarettes. The patent was involved in litigation in the UK and Germany among various e-cigarette companies in the mid-2010s because it represents an early example of an e-cigarette patent which covered modern e-cigarette designs.
The patent was based on a PCT application WO2007131449, originally drafted in Chinese. Unfortunately, the Chinese text itself was less than satisfactory, and the English translation submitted on entry into the European phase was also of limited quality. This later led to numerous added matter issues under Article 123(2) EPC.
Translation issues and Added Matter disputes
Air Inlet(s)
The Opponents objected that the application did not disclose an electronic cigarette having a single air inlet. The patentee explained that the Chinese characters 进气孔used to refer to the air inlets in the original Chinese implicitly referred to “one or more air inlets” because in Chinese if a specific number of air inlets was to be intended this would need to be made explicit in the Chinese (e.g. 一个进气口 one air inlet or 两个进气孔 two air inlets).
“Perforated” vs “Porous”
The original translation rendered a key term 多孔 (“Duo Kong” two characters literally having separate meanings as “many” and “holes”) as “perforated,” later corrected to “porous.” The Opponents objected that this correction introduced added matter, a point that was upheld by the EPO in a related divisional case.


“Frame” vs “Support Member”
The Opponents objected that 架体 ( “Jia Ti” two characters literally having separate meanings as “frame” and “body”) had a restricted meaning of “frame” and that the translation of 架体 as “support member” added matter.
Conjunctions and Prepositions
Even small linguistic nuances triggered disputes. For example, the location of the air channel in the claim was objected to with an Opponent contending that the original Chinese referred to the air channel being located “in the centre on one end surface of a cigarette holder shell” rather than “in the centre of one end surface of a cigarette holder shell”. This objection was refuted by the patentee with an explanation that in the original Chinese it was clear the central air channel was located in the centre of the surface of the cigarette holder shell.
Resolution and practical lessons
Ultimately the EP Opposition against EP2022349 ended without a formal conclusion on these translation disputes, as the case was withdrawn prior to a final decision. Nevertheless, the case provides a valuable example of issues which can arise when an inaccurate translation is used as well as the manner in which such objections may be overcome – in this case affidavit evidence was filed to explain the differences between English and Chinese.
The EP2022349 Opposition is a cautionary tale for patentees, attorneys, and translators alike. Above all, it reinforces the importance of investing in precise translations and expert linguistic input at the earliest stages of international patent prosecution.

